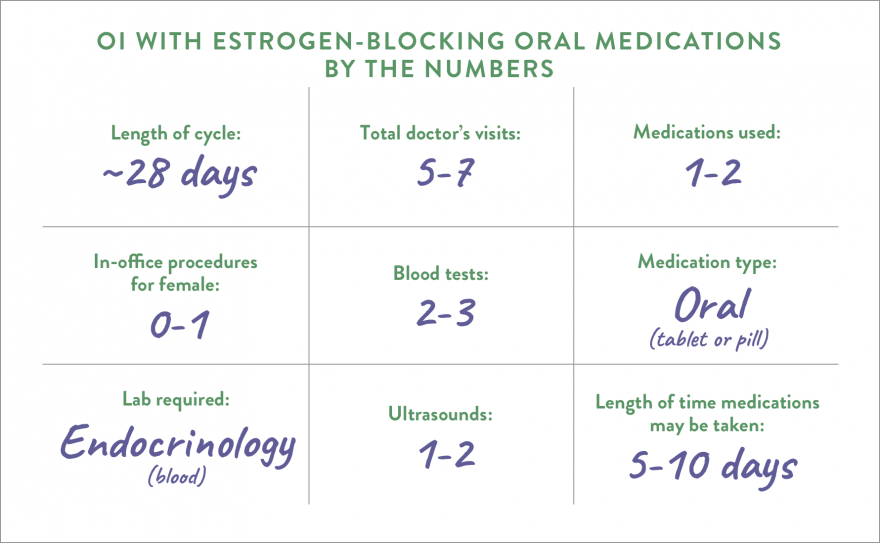
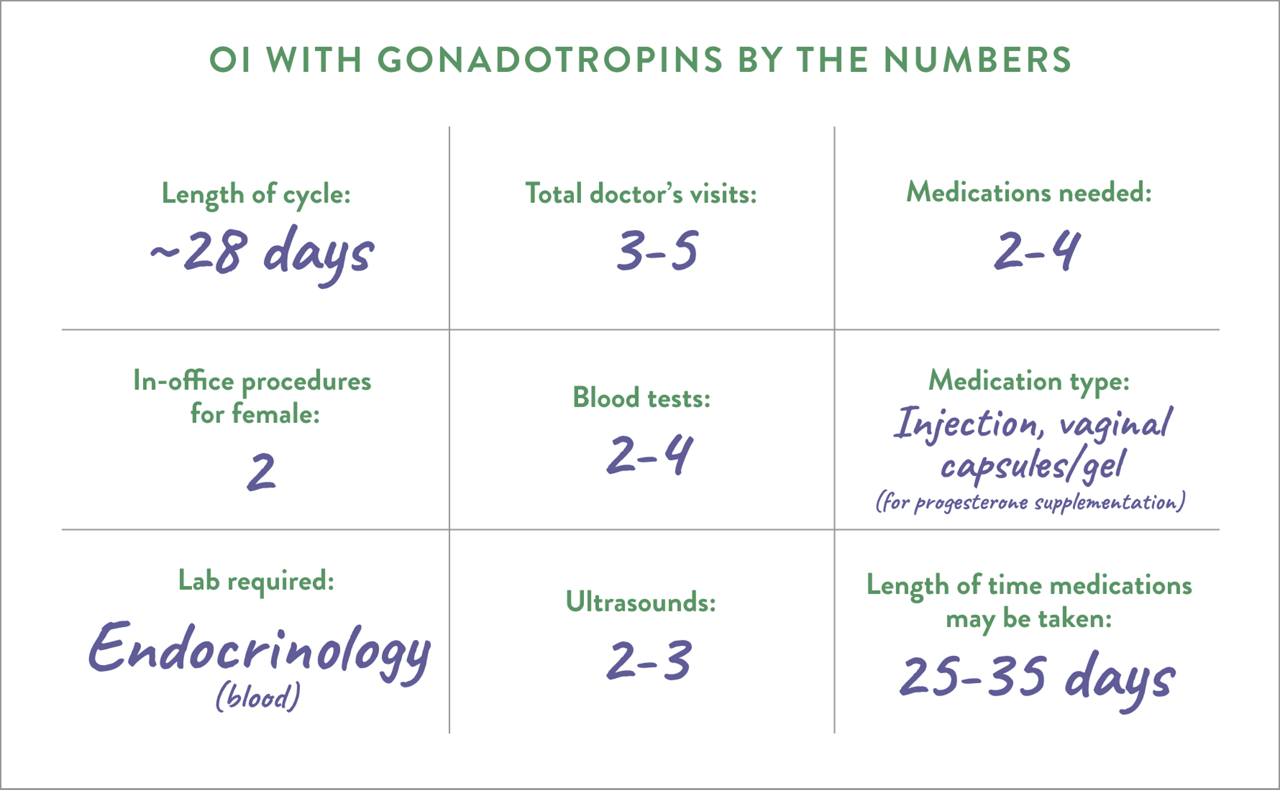
Estrogen blockers are pills or tablets taken by mouth. They work by triggering the pituitary gland, located in the brain, to make more follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). The additional FSH causes follicles—fluid-filled sacs containing eggs—to develop.
The follicles release estrogen as they grow, which eventually causes your pituitary gland to release a large amount of luteinizing hormone (LH). This LH surge causes the eggs in the most mature follicles to be released, which is called ovulation.